Troubleshooting
The following sections describe how to troubleshoot the Chef Infra Server, Chef Infra Client, and Chef Workstation.
401 Unauthorized
There are multiple causes of the Chef 401 “Unauthorized” error, so please use the sections below to find the error message that most closely matches your output. If you are unable to find a matching error, or if the provided steps are unhelpful, please file a help ticket.
Failed to authenticate as ORGANIZATION-validator
If you’re receiving an error like the following it most likely means you’ll need to regenerate the ORGANIZATION-validator.pem file:
INFO: Client key /etc/chef/client.pem isn't present - registering
INFO: HTTP Request Returned 401 Unauthorized: Failed to authenticate as ORGANIZATION-validator. Ensure that your node_name and client key are correct.
FATAL: Stacktrace dumped to c:/chef/cache/chef-stacktrace.out
FATAL: Net::HTTPClientException: 401 "Unauthorized"
Troubleshooting steps
Check if the ORGANIZATION-validator.pem file exists in one of the following locations:
~/.chef ~/projects/current_project/.chef /etc/chefIf one is present, verify that it has the correct read permissions.
If there’s no ORGANIZATION-validator.pem file, regenerate it.
Recreate this file by going to the Chef management console web user interface and selecting Organizations in the upper right side of the screen.
You can then select Reset Validation Key next to the organization for which the key is to be reset.
Failed to authenticate to
When the values for certain settings in the client.rb file—node_name and client_key—are incorrect, it won’t be possible to authenticate to the Chef Infra Server. An error similar to the following is shown:
ERROR: Failed to authenticate to https://api.opscode.com/organizations/ORGANIZATION as USERNAME with key /path/to/USERNAME.pem
Response: Failed to authenticate as USERNAME. Ensure that your node_name and client key are correct.
Troubleshooting steps
Verify you have the correct values in your config.rb file, especially for the
node_nameandclient_keysettings.Check if the file referenced in the
client_keysetting (usually USER.pem) exists. Some common locations include:~/.chef~/projects/current_project/.chef/etc/chefIf one is present, verify that it has the correct read permissions.
If there’s no client.rb file, regenerate it and ensure the values for the
node_nameandclient_keysettings are correct.
Organization not found
If you see this error when trying to recreate the ORGANIZATION-validator.pem, it’s possible that Chef Infra Client itself was deleted. In this situation, the ORGANIZATION-validator.pem will need to be recreated. In these directions, ORGANIZATION should be replaced with the name of your organization.
To reset a chef-validator key:
Open the Chef management console.
Click Policy.
Click Clients.
Select a chef-validator key.
Click the Details tab.
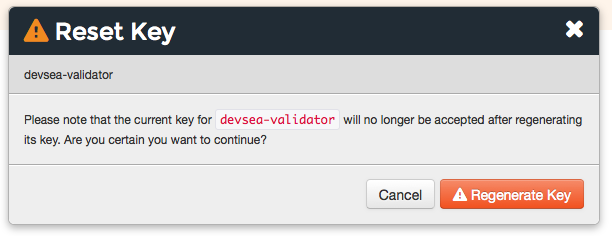
Click Reset Key.
In the Reset Key dialog box, confirm that the key should be regenerated and click the Reset Key button:
Copy the private key:
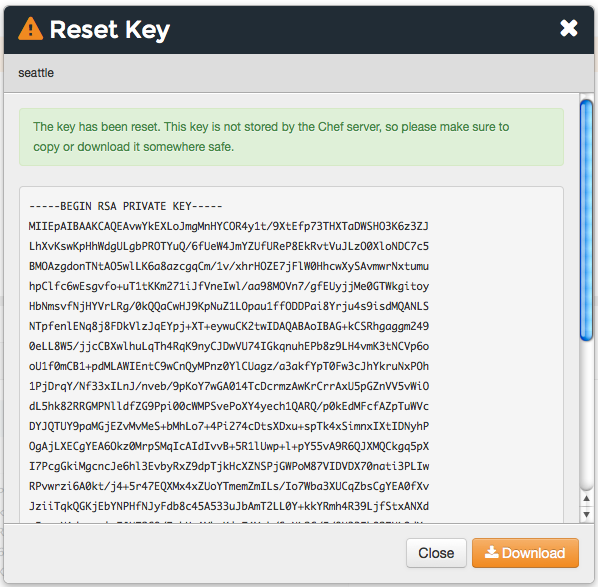
or download and save the private key locally:
Synchronize the clock on your host
If the system clock drifts more than 15 minutes from the actual time, the following type of error will be shown:
INFO: Client key /etc/chef/client.pem isn't present - registering
INFO: HTTP Request Returned 401 Unauthorized: Failed to authenticate as ORGANIZATION-validator. Synchronize the clock on your host.
FATAL: Stacktrace dumped to /var/chef/cache/chef-stacktrace.out
FATAL: Net::HTTPClientException: 401 "Unauthorized"
To resolve this error, synchronize the clock with an NTP server.
All other 401 errors
The general Net::HTTPClientException: 401 "Unauthorized" error will usually occur for one of two reasons.
Troubleshooting steps
Make sure your
client.pemis valid.This can be fixed by deleting
client.pemin/etc/chefand deleting the client and node with knife.On a management station:
# Dump the current node to JSON knife node show NODE_NAME -fJ > NODE_NAME.json knife client delete FQDN -y knife node delete FQDN -yOn an affected node (as root):
rm /etc/chef/client.pem chef-clientWhen Chef Infra Client runs, it will register the API client and generate the correct key.
After successfully running Chef Infra Client on the node, reload the
run_listand node attributes:knife node from file NODE_NAME.jsonMake sure to use the same
node_nameas the initial Chef Infra Client run.This can happen for a number of reasons. For example, if the client.rb file doesn’t specify the correct node name and the system’s hostname has changed.
Running
chef-client -l debugwill identify the node name being used by Chef Infra Client for authentication attempts:DEBUG: Signing the request as SOME_NODE_NAMEThis can be fixed by explicitly setting
node_namein the client.rb file to match the name originally used to register.node_node 'mynode.mycompany.com'Alternatively, re-register the node using the method described previously.
403 Forbidden
If you’re seeing output like this:
FATAL: Stacktrace dumped to /var/chef/cache/chef-stacktrace.out
FATAL: Net::HTTPClientException: 403 "Forbidden"
this is an indication that there is an issue with permissions on the Chef Infra Server.
Troubleshooting steps
In Chef, there are two different types of permissions issues, object specific and global permissions. To figure out which type of permission issue you’re experiencing, run Chef Infra Client again using the -l debug options to see debugging output.
You should see something like this up the stack trace:
DEBUG: Sending HTTP Request to https://api.opscode.com/organizations/ORGNAME/nodes
ERROR: Running exception handlers
The URL will help identify the type of permission issue. If the URL is an index action (that’s, operating on a collection of resources, like /nodes) then this is a global permission. If the URL is operating on an instance of a collection (/nodes/NODENAME) then this is an object permission issue.
To fix the global permissions:
Log in to the Chef management console and click on the failing object type (most likely Nodes).
Click on the Permissions sub-tab. Which permission it needs, depends on which request that failed:
GET - Under the group section, make sure it has the LIST permission checked POST - Under the group section, make sure it has the CREATE permission checked
Check the checkboxes needed and save the updates.
To fix object permissions:
Log in to the Chef management console and click on the failing object type (most likely Nodes).
Click on the object in the list that’s causing the error.
Click on the Permissions sub-tab. Which permission it needs, depends on the type of request that failed:
GET - Make sure it has the READ permission checked PUT - Make sure it has the UPDATE permission checked DELETE - Make sure it has the DELETE permission checked
Check the checkboxes needed and save the updates.
500 (Unexpected)
HTTP 500 is a non-specific error message. The full error message for the error Chef Infra Client is receiving can be found in one of the following log files:
/var/log/opscode/opscode-account/current/var/log/opscode/opscode-erchef/current
The error will likely found in a stacktrace from the application error. In some cases the error message will clearly indicate a problem with another service which can be investigated further. For non-obvious errors, please contact Chef and attach the log files.
502 / 504 (Gateway)
Determine which API service is returning 504s using the Nginx access logs. API requests returning 504 can be found with the following command on a frontend:
grep 'HTTP/1.1" 504' /var/log/opscode/nginx/access.log
The following will extract the URLs and sort them by uniq count:
grep 'HTTP/1.1" 504' nginx-access.log | cut -d' ' -f8 | sort | uniq -c | sort
In a large installation, you may need to restrict this to a subset of the requests:
tail -10000 nginx-access.log | grep 'HTTP/1.1" 504' | cut -d' ' -f8 | sort | uniq -c | sort
You can also use the ntail utility.
If the problematic service is a Ruby-based service and the frontend machines have free RAM or CPU, consider increasing the number of worker processes. If the problematic service is opscode-erchef, use the request log to determine whether a particular component of requests is slow.
Workflow Problems
In working with Chef, you’ll most likely encounter issues in your regular workflow. This page is a collection of common errors our users have reported while working with Chef. Please use the accordion below to select the error message that most closely matches your output. If you are unable to find a matching error, or if the provided steps are unhelpful, please file a help ticket.
No such file or directory
If you’re seeing an error like:
Client key /etc/chef/client.pem isn'tresent - registering
WARN: Failed to read the private key /etc/che/validation.pem: #<Errno::ENOENT: No such file or directory - /etc/chef/validation.pem>
FATAL: Stacktrace dumped to /etc/chef/cache/chef-stacktrace.out
FATAL: Chef::Exceptions::PrivateKeyMissing: I can't read /etc/chef/validation.pem, which you told me to use to sign requests
It means that Chef Infra Client couldn’t find your validation.pem.
Troubleshooting steps
- Make sure your
validation.pemorORGANIZATION-validator.pemis downloaded and accessible by the current user. - Make sure your client.rb points to the location of your validator pem.
Commit or stash your changes
This isn’t an error, but can be confusing to new users. When you try to install a cookbook with changes that you haven’t committed to Git, you will get this error:
Installing getting-started to /home/jes/chef-repo/.chef/../cookbooks
ERROR: You have uncommitted changes to your cookbook repo:
M cookbooks/getting-started/recipes/default.rb
?? .chef/
?? log
Commit or stash your changes before importing cookbooks
Troubleshooting steps
Solve this by committing the cookbook changes. For example, the following command would commit all new changes with the message “updates”.
git commit -am "Updating so I can install a site cookbook"
Re-run the knife supermarket install subcommand again to install the community cookbook.
Can’t find config file
If you’re seeing an error like:
WARN: ***************************************
WARN: Can not find config file: /etc/chef/client.rb, using defaults.
WARN: No such file or directory - /etc/chef/client.rb
# ... output truncated ... #
FATAL: Chef::Exceptions::PrivateKeyMissing: I can't read /etc/chef/validation.pem, which you told me to use to sign requests!
Troubleshooting steps
Work around this issue by supplying the full path to the client.rb file:
chef-client -c /etc/chef/client.rb
Pivotal.rb doesn’t exist
If you’re seeing an error like:
ERROR: CONFIGURATION ERROR:Specified config file /etc/opscode/pivotal.rb doesn't exist
Troubleshooting steps
Run the following to restart all of the services:
chef-server-ctl reconfigure
Because the Chef Infra Server is composed of many different services that work together to create a functioning system, this step may take a few minutes to complete.
External PostgreSQL
The following error messages may be present when configuring the Chef Infra Server to use a remote PostgreSQL server.
CSPG001 (changed setting)
Reason
The value of postgresql['external'] has been changed.
Possible causes
- This setting must be set before running
chef-server-ctl reconfigure, and may not be changed after
Warning
Resolution
- Back up the data using
knife ec backup, create a new backend instance, and then restore the data - Re-point frontend machines at the new backend instance or assign the new backend instance the name/VIP of the old backend instance (including certificates and keys)
CSPG010 (can’t connect)
Reason
Can’t connect to PostgreSQL on the remote server.
Possible causes
- PostgreSQL isn’t running on the remote server
- The port used by PostgreSQL is blocked by a firewall on the remote server
- Network routing configuration is preventing access to the host
- When using Amazon Web Services (AWS), rules for security groups are preventing the Chef Infra Server from communicating with PostgreSQL
CSPG011 (can’t authenticate)
Reason
Can’t authenticate to PostgreSQL on the remote server.
Possible causes
- Incorrect password specified for
db_superuser_password - Incorrect user name specified for
db_superuser
CSPG012 (incorrect rules)
Reason
Can’t connect to PostgreSQL on the remote server because rules in
pg_hba are incorrect.
Possible causes
- No
pg_hba.confrule exists for thedb_superuserin PostgreSQL - A rule exists for the
db_superuserinpg_hba.conf, but it doesn’t specifymd5access - A rule in
pg_hba.confspecifies an incorrect originating address
Resolution
Entries in the pg_hba.conf file should allow:
- All user names that originate from any Chef Infra Server instance using
md5authentication. - A specific application names:
$db_superuser(the configured superuser name in the chef-server.rb file),oc_id,oc_id_ro,opscode_chef,opscode_chef_ro,bifrost, andbifrost_ro
pg_hba.conf User Names
For example, a pg_hba.conf entry for a valid username and password from the 192.0.2.0 subnet:
host postgres all 192.0.2.0/24 md5
or, specific named users with a valid password originating from the 192.0.2.0 subnet. A file named $PGDATA/chef_users with the following content must be created:
opscode_chef
opscode_chef_ro
bifrost
bifrost_ro
oc_id
oc_id_ro
where CHEF-SUPERUSER-NAME is replaced with the same user name specified by postgresql['db_superuser']. The corresponding pg_hba.conf entry is similar to:
host postgres @chef_users 192.168.93.0/24 md5
or, using the same $PGDATA/chef_users file (from the previous example), the following example shows a way to limit connections to specific nodes that are running components of the Chef Infra Server.This approach requires more maintenance because the pg_hba.conffile must be updated when machines are added to or removed from theChef Infra Server configuration. For example, a high availability configuration with four nodes: backend-1 (192.0.2.100),backend-2 (192.0.2.101), frontend-1 (192.0.2.110), andfrontend-2 (192.0.2.111).
The corresponding pg_hba.conf entry is similar to:
host postgres @chef_users 192.0.2.100 md5
host postgres @chef_users 192.0.2.101 md5
host postgres @chef_users 192.0.2.110 md5
host postgres @chef_users 192.0.2.111 md5
These changes also require a configuration reload for PostgreSQL:
pg_ctl reload
or:
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
pg_hba.conf Application names
Rules in the pg_hba.conf file should allow only specific application names:
$db_superuser(the configured superuser name in the chef-server.rb file)oc_idoc_id_roopscode_chefopscode_chef_robifrostbifrost_ro
CSPG013 (incorrect permissions)
Reason
The db_superuser account has incorrect permissions.
Possible causes
The
db_superuseraccount hasn’t been grantedSUPERUSERaccessThe
db_superuseraccount hasn’t been grantedCREATE DATABASEandCREATE ROLEprivilegesALTER ROLE "$your_db_superuser_name" WITH SUPERUSERor:
ALTER ROLE "$your_db_superuser_name" WITH CREATEDB CREATEROLE
CSPG014 (incorrect version)
Reason
Bad version of PostgreSQL.
Possible causes
- The remote server isn’t running PostgreSQL version 9.2.x
CSPG015 (missing database)
Reason
The database template template1 doesn’t exist.
Possible causes
- The
template1database template has been removed from the remote server
Resolution
Run the following command (as a superuser):
CREATE DATABASE template1 TEMPLATE template0or:
createdb -T template0 template1
CSPG016 (database exists)
Reason
One (or more) of the PostgreSQL databases already exists.
Possible causes
- The
opscode_chef,oc_id, and/orbifrostdatabases already exist on the remote machine - The PostgreSQL database exists for another application
Resolution
- Verify that the
opscode_chef,oc_id, and/orbifrostdatabases exist, and then verify that they’re not being used by another internal application - Back up the PostgreSQL data, remove the existing databases, and reconfigure the Chef server
CSPG017 (user exists)
Reason
One (or more) of the PostgreSQL predefined users already exists.
Possible causes
- The
opscode_chef,ospcode_chef_ro,bifrost,bifrost_ro,oc_id, oroc_id_rousers already exist on the remote machine - The
postgresql['vip']setting is configured to a remote host, butpostgresql['external']isn’t set totrue, which causes theopscode_chefandospcode_chef_rousers to be created before the machine is reconfigured, which will return a permissions error - Existing, valid naming conflicts are present, where the users were created independently of the Chef server
Resolution
Run the following, if it’s safe to do so, to update the user name that’s specified in the error message:
DROP ROLE "name-of-user";or change the name of the user by updating following settings in the chef-server.rb configuration file:
oc_id['sql_user'] = 'alternative_username' oc_id['sql_ro_user'] = 'alternative_username_for_ro_access' opscode_erchef['sql_user'] = 'alternative_username' opscode_erchef['sql_ro_user'] = 'alternative_username_for_ro_access' oc_bifrost['sql_ro_user'] = 'alternative_username' oc_bifrost['sql_ro_user'] = 'alternative_username_for_ro_access'