Chef Manage

Warning
Chef Manage is deprecated and no longer under active development. It’s supported on Chef Automate installations up to version 1.8 and replaced by Chef Automate 2.0. Contact your Chef account representative for information about upgrading your system. See our Automate documentation to learn more about Chef Automate 2.
This document is no longer maintained.
Note
The Chef management console enables the management of nodes, data bags, roles, environments, and cookbooks by using a web user interface. In addition, access to nodes, data bags, roles, environments, and cookbooks is configurable using role-based access control (RBAC).
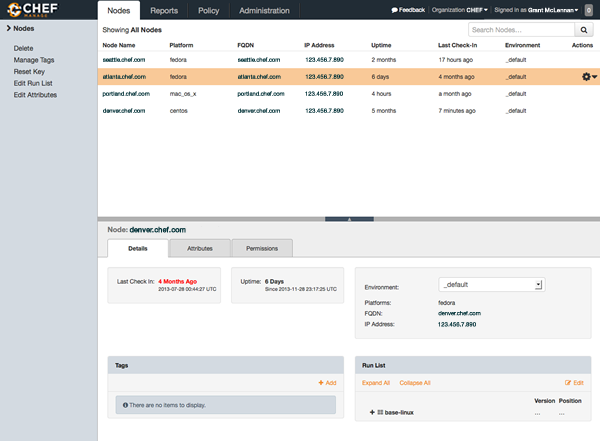
Nodes
A node is any device—physical, virtual, cloud, network device, etc.—that’s under management by Chef Infra.The Chef management console provides ways for users to delete nodes and reset their private keys, edit node attributes, manage the run-lists, configure user and group permissions, and manage tags.
Search
Search indexes allow queries to be made for any type of data that’s indexed by the Chef Infra Server, including data bags (and data bag items), environments, nodes, and roles. A defined query syntax is used to support search patterns like exact, wildcard, range, and fuzzy. A search is a full-text query that can be done from several locations, including from within a recipe, by using thesearch subcommand in
knife, the search method in the Chef Infra Language, the search box in the Chef
management console, and by using the /search or /search/INDEX
endpoints in the Chef Infra Server API. The search engine is based on
Elasticsearch and is run from the Chef Infra Server.Note
Query Syntax
A search query is comprised of two parts: the key and the search pattern. A search query has the following syntax:
key:search_pattern
where key is a field name that’s found in the JSON description of an
indexable object on the Chef Infra Server (a role, node, client,
environment, or data bag) and search_pattern defines what will be
searched for, using one of the following search patterns: exact,
wildcard, range, or fuzzy matching. Both key and search_pattern are
case-sensitive; key has limited support for multiple character
wildcard matching using an asterisk ("*") (and as long as it’s not the
first character).
Keys
A field name/description pair is available in the JSON object. Use the field name when searching for this information in the JSON object. Any field that exists in any JSON description for any role, node, Chef Infra Client, environment, or data bag can be searched.Nested Fields
A nested field appears deeper in the JSON data structure. For example,
information about a network interface might be several layers deep:
node['network']['interfaces']['en1']. When nested fields are present
in a JSON structure, Chef Infra Client will extract those nested fields
to the top-level, flattening them into compound fields that support
wildcard search patterns.
By combining wildcards with range-matching patterns and wildcard queries, it’s possible to perform powerful searches, such as using the vendor part of the MAC address to find every node that has a network card made by the specified vendor.
Consider the following snippet of JSON data:
{"network":
[
//snipped...
"interfaces",
{"en1": {
"number": "1",
"flags": [
"UP",
"BROADCAST",
"SMART",
"RUNNING",
"SIMPLEX",
"MULTICAST"
],
"addresses": {
"fe80::fa1e:dfff:fed8:63a2": {
"scope": "Link",
"prefixlen": "64",
"family": "inet6"
},
"f8:1e:df:d8:63:a2": {
"family": "lladdr"
},
"192.0.2.0": {
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"broadcast": "192.168.0.255",
"family": "inet"
}
},
"mtu": "1500",
"media": {
"supported": {
"autoselect": {
"options": [
]
}
},
"selected": {
"autoselect": {
"options": [
]
}
}
},
"type": "en",
"status": "active",
"encapsulation": "Ethernet"
},
//snipped...
Before this data is indexed on the Chef Infra Server, the nested fields are extracted into the top level, similar to:
"broadcast" => "192.168.0.255",
"flags" => ["UP", "BROADCAST", "SMART", "RUNNING", "SIMPLEX", "MULTICAST"]
"mtu" => "1500"
which allows searches like the following to find data that’s present in this node:
node "broadcast:192.168.0.*"
or:
node "mtu:1500"
or:
node "flags:UP"
This data is also flattened into various compound fields, which follow
the same pattern as the JSON hierarchy and use underscores (_) to
separate the levels of data, similar to:
# ...snip...
"network_interfaces_en1_addresses_192.0.2.0_broadcast" => "192.168.0.255",
"network_interfaces_en1_addresses_fe80::fa1e:tldr_family" => "inet6",
"network_interfaces_en1_addresses" => ["fe80::fa1e:tldr","f8:1e:df:tldr","192.0.2.0"]
# ...snip...
which allows searches like the following to find data that’s present in this node:
node "network_interfaces_en1_addresses:192.0.2.0"
This flattened data structure also supports using wildcard compound
fields, which allow searches to omit levels within the JSON data
structure that aren’t important to the search query. In the following
example, an asterisk (*) is used to show where the wildcard can exist
when searching for a nested field:
"network_interfaces_*_flags" => ["UP", "BROADCAST", "SMART", "RUNNING", "SIMPLEX", "MULTICAST"]
"network_interfaces_*_addresses" => ["fe80::fa1e:dfff:fed8:63a2", "192.0.2.0", "f8:1e:df:d8:63:a2"]
"network_interfaces_en0_media_*" => ["autoselect", "none", "1000baseT", "10baseT/UTP", "100baseTX"]
"network_interfaces_en1_*" => ["1", "UP", "BROADCAST", "SMART", "RUNNING", "SIMPLEX", "MULTICAST",
"fe80::fa1e:dfff:fed8:63a2", "f8:1e:df:d8:63:a2", "192.0.2.0",
"1500", "supported", "selected", "en", "active", "Ethernet"]
For each of the wildcard examples above, the possible values are shown contained within the brackets. When running a search query, the query syntax for wildcards is to simply omit the name of the node (while preserving the underscores), similar to:
network_interfaces__flags
This query will search within the flags node, within the JSON
structure, for each of UP, BROADCAST, SMART, RUNNING, SIMPLEX,
and MULTICAST.
About Patterns
A search pattern is a way to fine-tune search results by returning anything that matches some type of incomplete search query. There are four types of search patterns that can be used when searching the search indexes on the Chef Infra Server: exact, wildcard, range, and fuzzy.Exact Matching
An exact matching search pattern is used to search for a key with a name that exactly matches a search query. If the name of the key contains spaces, quotes must be used in the search pattern to ensure the search query finds the key. The entire query must also be contained within quotes, so as to prevent it from being interpreted by Ruby or a command shell. The best way to ensure that quotes are used consistently is to quote the entire query using single quotes (’ ‘) and a search pattern with double quotes (" “).Wildcard Matching
A wildcard matching search pattern is used to query for substring matches that replace zero (or more) characters in the search pattern with anything that could match the replaced character. There are two types of wildcard searches:
- A question mark (
?) can be used to replace exactly one character (as long as that character isn’t the first character in the search pattern) - An asterisk (
*) can be used to replace any number of characters (including zero)
Range Matching
A range matching search pattern is used to query for values that are within a range defined by upper and lower boundaries. A range matching search pattern can be inclusive or exclusive of the boundaries. Use square brackets ("[ ]") to denote inclusive boundaries and curly braces ("{ }") to denote exclusive boundaries and with the following syntax:
boundary TO boundary
where TO is required (and must be capitalized).
Fuzzy Matching
A fuzzy matching search pattern is used to search based on the proximity of two strings of characters. An (optional) integer may be used as part of the search query to more closely define the proximity. A fuzzy matching search pattern has the following syntax:
"search_query"~edit_distance
where search_query is the string that will be used during the search
and edit_distance is the proximity. A tilde ("~") is used to separate
the edit distance from the search query.
About Operators
An operator can be used to ensure that certain terms are included in the results, are excluded from the results, or aren’t included even when other aspects of the query match. Searches can use the following operators:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
AND | Use to find a match when both terms exist. |
OR | Use to find a match if either term exists. |
NOT | Use to exclude the term after NOT from the search results. |
Operators must be in ALL CAPS. Parentheses can be used to group clauses and to form sub-queries.
Warning
Using AND NOT together may trigger an error. For example:
ERROR: knife search failed: invalid search query:
'datacenter%3A123%20AND%20NOT%20hostname%3Adev-%20AND%20NOT%20hostanem%3Asyslog-'
Parse error at offset: 38 Reason: Expected one of \ at line 1, column 42 (byte 42) after AND
Use - instead of NOT. For example:
knife search sample "id:foo AND -id:bar"
Special Characters
A special character can be used to fine-tune a search query and to
increase the accuracy of the search results. The following characters
can be included within the search query syntax, but each occurrence of a
special character must be escaped with a backslash (\), also (/)
must be escaped against the Elasticsearch:
+ - && | | ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ /
For example:
\(1\+1\)\:2
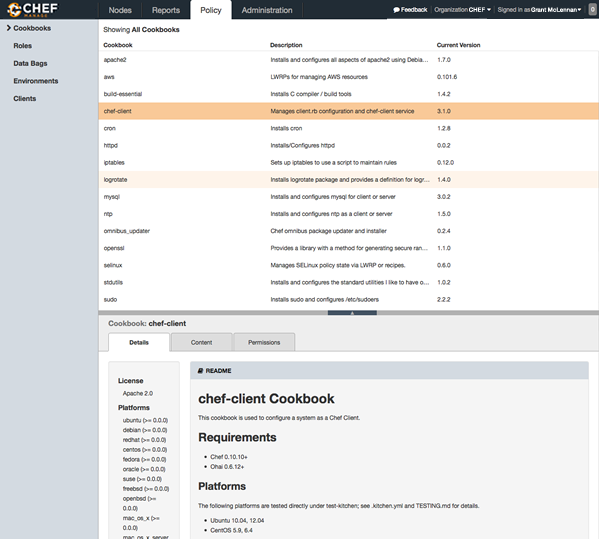
Policy
Policy maps business and operational requirements, process, and workflow to the following settings and objects stored on the Chef Infra Server:
- Roles define server types, such as “web server” or “database server”.
- Environments define process, such as “dev”, “staging”, or “production”.
- Attributes define environment-specific details about a node that are included in a Policyfile.
- Certain types of data—passwords, user account data, and other sensitive items—can be placed in data bags, which are located in a secure sub-area on the Chef Infra Server that can only be accessed by nodes that authenticate to the Chef Infra Server with the correct SSL certificates.
- The cookbooks (and cookbook versions) in which organization-specific configuration policies are maintained.
The Chef management console provides ways for users to manage data bags, environments, roles, cookbooks, clients, and managing tags.
Admin
Organizations, users, and groups can be managed from the Chef management console, including role-based access control for any user and group to any of the objects saved to the Chef Infra Server.
The Chef Infra Server uses role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to objects—nodes, environments, roles, data bags, cookbooks, and so on. This ensures that only authorized user and/or Chef Infra Client requests to the Chef Infra Server are allowed. Access to objects on the Chef Infra Server is fine-grained, allowing access to be defined by object type, object, group, user, and organization. The Chef Infra Server uses permissions to define how a user may interact with an object, after they have been authorized to do so.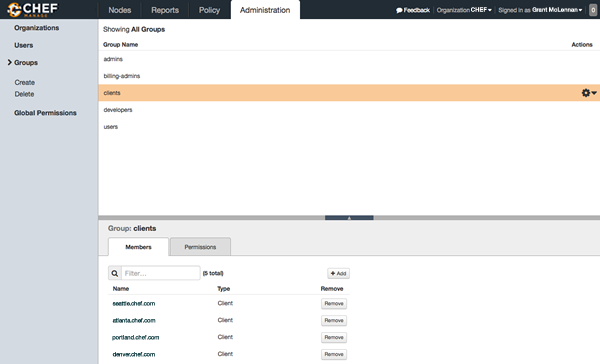
Install Chef Manage
The install subcommand downloads packages from https://packages.chef.io by default.
For systems that are not behind a firewall (and have connectivity to https://packages.chef.io), these packages can be installed as described below.
Install add-ons
Install Chef Manage with:
sudo chef-server-ctl install chef-manageReconfigure the server
sudo chef-server-ctl reconfigureReconfigure add-ons
Reconfigure Chef Manage with:
sudo chef-manage-ctl reconfigure
Finally, accept the Chef License:
sudo chef-manage-ctl reconfigure --accept-license
Chef Manage Local Installation
Use the install subcommand with the --path option to install the Chef Manage (chef-manage) add-on for Chef Infra Server.
sudo chef-server-ctl install PACKAGE_NAME --path /path/to/package/directory
For example:
sudo chef-server-ctl install chef-manage --path /root/packages
The chef-server-ctl command will install the first chef-manage
package found in the /root/packages directory.